The funnel (AARRR Funnel) is sometimes known as the sales funnel; the marketing funnels, the digital final; at the end, it’s all a final. What was going to be taking a closer look at is the AARRR framework. The AARRR framework. It is a widely used and practiced element in the growth hacking area.
Overall this is a common practice; many organizations have taken this and highly optimized eight and have taken it to the next level. What we are going to look at is not just the final but a growth system. I funnel a component of a growth system. At the core of this is managing the customer journey.
A growth system brings all the processes and moving parts within an organization that works on growth into a single system.
Before we get started, here is some background information to around you off.
- What is growth hacking?
- Why is growth hacking important?
- How does growth hacking work?
- When should growth hacking be used?
- How to develop the skills to hack growth?
Subscribe for updates
What is growth hacking? – AARRR FUNNEL
Growth hackers explore new growth opportunities systematically at any point of the customer journey, from awareness through the market to brand ambassadors by optimizing the product.
In terms of technology, it originated in 2010 when Sean Ellis coined it is mostly used by startups because of its limited budgets and limited resources. Since then, it has shown an incredible increase in popularization among large-scale and traditional businesses.
Companies like Shopify like Uber has their own head of growth and dedicated growth team. The growth hacker is based on an experiment-based, data-driven.
There is a wide range of definitions. In the Book Ready Set Growth Hack, growth hacking is defined at a strategic level as a process that achieved disproportional results.
This is best understood through an example of efforts v.s results. This is when less effort is exerted to get dispositional results.
How does growth hacking work?
Growth hacking works and is defined in the Ready Set Growth Hack as a systematic process governed by the growth cycle concept.
The growth cycle is a three-phase process, where it starts with a growth problem, moves into experimentation then into scaling.
Based on this process, once a growth problem is well defined through a specific process, it would then be up to the growth hacker to find solutions. Solutions are found vis structured and systematic experimentations.
Using growth analytics for data-driven growth decisions, growth hackers can quickly discover what works and doesn’t before investing a penny in more development. This is governed by a process called growth thinking which is a design methodology used for growth hacking.
What is a funnel?
A funnel is part of a growth system; see below for more information. The fundamental difference between a funnel in a growth system is that one is linear, and the other is cyclical in nature. A funnel is linear; meanwhile, a growth system is cyclical.
This is important to understand as many growth marketers have been focused exclusively on the final without seeing it as part of the whole growth system.
What is a growth system?
A funnel is part of a growth system within an organization. A growth system is a drill-down, filter-style process. Growth marketers usually just focused on the funnel but not the whole growth system. The growth system is where all of this comes together:

1. Visibility is getting your brand and offering in front of prospects that may have an interest in your offering.
2. Interest is transforming visibility into a desirable attitude towards your offering that engages potential customers.
3. Qualify transforms desire into potential sales by filtering potential customers among those who would want to buy now, later on, or may need some encouragement to buy.
4. Convert is the transformation of qualified customers into actual revenue.
5. Loyalty is about customer service support and recycling the growth process. It transforms existing customers into greater revenue or a channel where you can generate increased sales through their own network or endorsement of your offerings.
The growth system is a systematic drill-down process that quickly, efficiently, and cost-effectively turns potential interest into revenue.
What is important about a successful growth system is its ability to do two main things. First is having a high conversion rate and the ability to convert loyalty to more sales.
How do a funnel and a growth system work together?
A funnel is a component of a growth system. The fundamental difference is that a final is linear in nature in a cyclical growth system. You cannot operate with a linear model; you need a growth system.
Therefore, a funnel is part of a graph system where the growth system can use the vinyl in a cyclical manner where can take a customer from the beginning of their journey all the way to the end and repeat I over and over.
Where did funnels begin?
The funnel, better known as the sales or marketing funnel, has been used for a long time. The origins of the sales or marketing funnel date back to the late 1800s. It was a process that was designed to manage sales and marketing activities.
Its starting point was how to manage the sales process from start to end. In the early 1900s, with the emergence of management consulting firms, the sales funnel started to take shape.
It started to take shape because organizations needed to understand their sales process and improve their final results. With the ultimate focus on revenue, the process would be broken down into smaller faces that would move a customer from visibility to a pate customer and eventually a loyal customer that would refer more business.
It is the same way it had started in today’s world, but the tools we use today are much more sophisticated.
One of the biggest advantages we have today is data and data analytics, which allows us to measure what parts of the final work are not working. Acquisition metrics is a more moderate nine is the terminology used for the same thing.
What is a good funnel vs. a bad funnel?
A good final has the ability to measure every step in a highly objective way. In this particular case, pirate metrics. The Pirate Metrics” framework founded by David McClure at PayPal is better known as the AARRR framework or the pirate funnel; framework.
The AARRR – Pirate Metrics allows for better management through measurements. As simple as that may sound, the pirate metrics play a crucial role in optimizing the final.
A good pirate funnel can demonstrate where there would be a bottleneck or even an area where something is performing very well; this data is consistent information to a growth factor to optimize the final where it needs to be.
A good funnel is all about identifying the paying customer to manage that journey from start to finish. A bad funnel is not able to create paying customers. This is an obvious distinction between what works and what doesn’t work very well.
Why should you have a funnel?
Your business model is dependent on it. A good business model enables and optimizes revenue from starting the AARRR private funnel / AARRR framework to the end.
Subscribe for updates
What is AARRR & Why is it popular?
AARRR means Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Referral, and Revenue and pirate funnel for understanding your customers, their journey/experience, and optimizing for valuable and actionable metric goals for your startup. THE AARRR or Pirate funnel is explained in simple terms:
Acquisition — “Where Are Our Users / Customers Coming From?”
- the most fundamental element here is to understand where you can gain visibility and be able to get a response to the visibility
- once you have that visibility and you see an initial response ensuring that the quality of the response or target customers align
- finally, it’s ensuring that you have a sizeable and scalable addressable audience of customers or users
Activation — “How good is the user’s / customer’s first experience?”
- this is a matter of aligning your offering with that that would solve a direct problem for a consumer
- the quicker and better you’re able to communicate value to solving a problem for customers, the quicker you be able to activate them
- their first impression is the lasting impression developing an experience where you can deliver that value and solve the problem quickly is vital
Retention — “How many of your customers are you retaining, and why are you losing the others?”
- What are you doing to ensure that customers could pay and stay longer?
- What are the triggers that not also keep a customer longer but gets a customer to continue to spend more
- How to dig deeper into solving their problem while creating more value that naturally signals a customer to want to stay longer and spend more money with you.
Referral — “How can you turn your customers into your advocates?”
- Which customers are those who would be most ideal for representing your brand and bringing in more customers
- What would be the triggers? An incentive is required to get customers to take action on your behalf and get you more customers.
- How to root word customers for taking action not just for getting you a new customer but speaking well about your brand and making you look good to get other customers
Revenue — “How can you increase revenue?”
- Identifying new products or services that can add value to your existing customers that they would be willing to pay for
- Identifying additional pain points where value could be created on top of what you are already doing for your existing customers
- How to upgrade and update customers buying Hansing what they’re ready you stew and really like but in a much better way
You can design a highly optimized final by addressing these different points in the final and digging deeper into understanding the trigger points.
Optimizing this is all about data and data analytics by making data-driven decisions on knowing where and how to optimize different parts of your final.
At the center of this is the customer journey, which is the process outlined in the funnel but, more importantly, the handover points between different phases in the funnel.
The conversion rate is about keeping the customer acquisition cost low. Second is having the ability to convert more existing customers into more business, as these two factors are vital in profitable and scalable growth.
Metrics effectively measure not just each part of the process of the handover points. The handover points are when you transition from every phase in AARRR FUNNEL. If you miss out on the handover points, you can lose paying customers easily.
Understanding the customer lifetime value of a new customer and an existing customer makes that handover points to valuable optimization bottlenecks within the funnel.
Applying Pirate Metrics
Pirate Metrics is a guideline that helps business owners determine the most important metric for the business. These metrics can help you simplify this complicated process and stay on track. Learning these data is one way to scale and maintain your business efficiently.
Optimizing your funnels may help you realize the crucial stages at which the customer interacts with your business. Therefore knowing how to react must be paramount. At worst, knowing those things will give you a way to scale. Let’s dig in a bit deeper into what to measure across the AARRR framework:
Acquisition — “Where Are Our Users / Customers Coming From?”
- Number of customers
- Number of visitors into unique vs. returning visitors
- Channels they are coming through
- Customers per channel
- Customers per channel – the first time
- Customers per channel – returning
- Customers per channel – bounce rate or how long they sat
- Customers per channel – spend
- Customers per channel -referrals
- Customers per channel -location
Activation — “How good is the user’s / customer’s first experience?”
- How long do they stay
- How many bounces or leave
- Stay – duration
- Stay – location
- Stay – profile
- Stay – revenue
- Stay – return
- Bounces – duration
- Bounces – location
- Bounces – profile
Retention — “How many of your customers are you retaining, and why are you losing the others?”
- How many are retained?
- How long they retain for
- If they retain, how much do they spend over their lifetime
- If they are retained do they bing, other customers
- If they are retained do promote your products/services
- If they are NOT retained – a financial reason
- If they are NOT retained – experience reason
- If they are NOT retained – value reason
- If they are NOT retained – a competitive reason
- If they are NOT retained – another reason
Referral — “How can you turn your customers into your advocates?”
- Who do they refer you to
- Do they refer you to a different type of customer
- Do different types of customers represent a new demographic to purse
- Why do they refer you – service advantages
- Why do they refer you – availability
- Why do they refer you – reach
- Why do they refer you – value alignment
- Why do they refer you – incentive
- Why do they refer you – competitive reasons
- Why do they refer you – by mistake
Revenue — “How can you increase revenue?”
- Make new products and services.
- Enhance existing products and services
- How to do more of what you’re doing well
- How to find another paying customer
- How to make it easier for potential customers
- Get new customers in different channels
- Get new customers in different locations
- Get new customers in different needs
- Get new customers at different price points
- Get new customers in different offering levels
Using the above metrics as a checklist will help you measure the right things today and use today’s data to explore future opportunities for growth.
These measures serve as an essential part of your business model; not all these measures will make sense to you, so it’s not about using all of them but rather using the right ones. Your target should be using 3 to 5 can’t call the measures across the whole AARRR framework.
48 things to considerations to optimize your funnel
- a conversion funnel is another word for a sales funnel
- a funnel is not a marketing strategy nor the other way around
- a funnel is not a growth strategy nor the other way around
- managing business growth is why a funnel exists.
- retention rate is the number of people you’re able to keep compared to the total
- a funnel focuses on developing real value
- drive growth via a funnel isn’t though you need a growth system
- don’t focus on new users only; new users need to be replicated
- vanity metrics are numbers that do not impact growth at all but make you look amazing
- one customer is all you need to start with
- long term growth is the name of the game, not short term
- A sign up is always worth something; it’s not free to focus on good quality sign up
- traction channel is a channel where results are coming from and can grow
- site visitors are not users, nor are they customers
- many businesses do not have a funnel to start with; if that is, you design one
- pay attention to handover metrics in the funnel
- successful today is not success tomorrow keep consistent
- widely accepted standards are good but are not where growth will always be
- non monetary platforms can always find a financial model to make them profitable
- a qualified lead is key, and increasing those are what impact the qualify of your whole funnel
- look beyond google ads/Facebook ads; there are many other lower-cost channels
- even a basic referral program works; don’t wait for a perfect referral program
- a funnel is not exclusive to a saas business or saas company only
- focus on creating incredible value
- get your target audience right
- nail down user engagement from day one
- how many customers do you have today is not tomorrow? Get focused
- master user behavior data is a good investment
- customer refers essentially; do not overlook them at all at anytime
- users acquired is not a customer acquired
- customer acquisition rate is how man potential customers your turn into revenue
- do not I am to be a huge advertising business only find other means for revenue
- tracking product marketing is vital; do not leave this aside
- a company’s growth is not about one thing, only about make it all work together well
- acquisition stage should not be the only focus, even if its the most important part right now
- a potential customer is as important as an existing customer
- a potential customer always opens up new doors of revenue beyond just themselves
- marketing efforts cannot be the funnel only
- use other channels don’t focus on one only
- find the one powerful aha moment and use it wisely
- driving growth isn’t based on a single thing, experiment on everything you can
- don’t ignore churn rate across all measures
- define your important metrics very early on
- need to keep stage focuses at all levels at all times to find growth
- A funnel is not for saas businesses only
- activation stage is vital to making the whole funnel work; get this one right
- most users fall off the funnel at the activation stage
- average refers happen within the first 14 days of the user journey
What is RARRA?
RARRA is a reworking of the core items of AARRR to prioritize what is most important rather than what comes first. Can I bring my visitors back again after a while to use the same app?
If you answered yes, you are actually working to build your customer base. You can measure your clients’ recurring presence by showing they continue to come back.
When we prioritize our retention, we build a real, permanent users base. Let us see that this can actually happen. In an interview last September, AARRA aimed to improve retention and gain market share. Let it be all the more annoying not to see him return.
Subscribe for updates
Why is AARRR Pirate Metrics no longer effective for mobile apps?
In 2008 only 500 app store apps existed, and their purchase was incredibly cheap. This landscape is drastically different today, and acquisition cost is no longer dirt cheap. In the current landscape, an acquisition-oriented growth model makes no sense.
We need a better model — and this model is the RARRA model based on data-based growth and data-driven growth. The average app loses 77% of its daily active users within the first three days of installation. They lost almost 90% – and they’re on the verge of bankruptcy. It’ll reach almost 95% of users in the first week.
Why do I need AAARRR?
The AAARRR framework also named the A3R3 system, can reduce the company in six stages; awareness development acquisition – Activation recruitment, and reference. If you fill in all the numbers, you will see what part of the sale funnel hurts the most.
Any change that you make in your navigation software helps you improve and consequently your growth. Ready for more tips about growth hacks online? Then the Pirate Funnels is ideal for you!
Accelerated growth methodologies and why they are rare
There are four primary categories of business methodologies. From the image provided below, you will notice using data taken in the inventory of this is methodologies, the usage of them that exhilarated growth methodologies are rare.
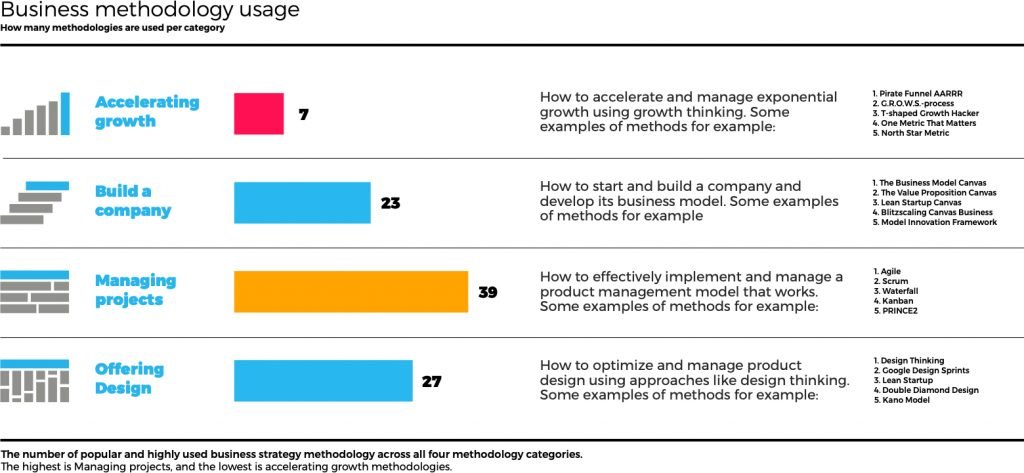
As counterintuitive as it may sound, the reality is that there is very little work done in the area of methodologies for exhilarating growth.
One of the main reasons behind this is that it has been as soon that many other methodologies would cover growth within them.
Although many of them hint at points
towards growth, none of them are dedicated towards the business model methodology design for exhilarated growth.
There are four types of methodologies to compare growth thinking.
- Offering design models to design products and services
- Managing projects models design to manage development
- Building a company models design for building a company
- Accelerating Growth models designed to accelerate the growth process
Compare Growth Thinking helps you understand the difference between, Business models, product management, project management, and design.
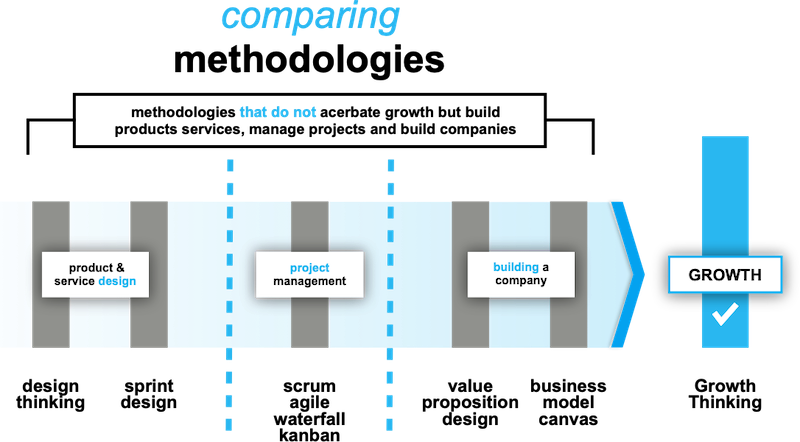
Four types of methodologies And all work with growth thinking
That is the good news whether you’re using them for product management, product design growth think is an add-on, or can even be stand-alone; if you want to accelerate your growth, the growth thinking design system is for you.
Learn more about the different models covering some of the most popular models, ones your probably already suing and have been trained on.
Accelerating growth
These models are designed to speed up growth by simplifying and systematizing their growth process.
- Pirate Funnel AARRR
- G.R.O.W.S.-process
- T-shaped Growth Hacker
- One Metric That Matters
- North Star Metric
Build a company
These models are business model-oriented methods designed to start a company.
- The Business Model Canvas
- The Value Proposition Canvas
- Lean Startup Canvas
- Blitzscaling Canvas Business
- Model Innovation Framework

Managing projects
These models help increase the success rate of product management and execution.
- Agile
- Scrum
- Waterfall
- Kanban
- PRINCE2
Offering Design
These models help design and improve products and services.
- Design Thinking
- Google Design Sprints
- Lean Startup
- Double Diamond Design
- Kano Model

Funnels work
Funnels only work when you have a growth system in place. Keep in mind that a final is on the linear application within a growth system.
Finals, better known as sales funnels, come in many shapes, sizes, and forms, and I refer to them in many different terminologies.
This article helps to create clarity between the AARRR framework as one of the types of finals to be used.
===========
Introduction to growth thinking — growth by design, how to thinking design, and growth hack.
GROWTH BY DESIGN – Most Growth Hackers struggle to get traction for new ideas. A lack of guidance and exact next steps are to blame. Imagine if you could grow a new concept from beginning to end, with a framework to move from thought and action in a fast, simple, and low-cost approach. Actioning ideas with precision isn’t easy; with the growth thinking, science-backed design system built by the top minds in growth hacking, it’s a simple, well-structured yet creative system that allows you to find growth.
Growth thinking is a fast, easy, and simple way to prototype growth hacks. This enables growth by visualizing a growth hack in abstract and then detailing them into a systematic approach. This makes it easy to develop and improve growth hacks and generate new, better growth hacks.
Benefits of the growth thinking design methodology —
- From idea to action – accurately and rapidly turn growth hacking ideas into execution quickly and cost-effectively,
- Think at scale – quickly and effortlessly find methods to take an abstract growth hack, structure it, scale it, and
- Save time and money – rapidly prototype your growth hacking ideas saving time and money.
This methodology uses a design system that Visualization, Systemize, Optimization, helps Rapid development, and instills Collaboration.






