Mastering the growth process is not easy. Growth hacking experts may vary in opinion when it comes to growth hacking. In this article, we will look at the fundamentals of what growth hacking is how it works in the four types of growth hacking. After that, we will look at the growth hacking process, scalability top line versus bottom line growth ethical hacking, and the growth factor mindset. What we will cover —
- What is growth hacking?
- How does growth hacking work?
- Four types of growth hacks
- How does the growth hacking process work?
- Understanding Scalability
- Topline vs. Bottom line growth and growth hacking
- What is ethical hacking
- The growth hacker and making the growth hacking process work.
Before we get started, some helpful background to growth hacking
- What is growth hacking?
- Why is growth hacking important?
- How does growth hacking work?
- When should growth hacking be used?
- How to develop the skills to hack growth?
What is growth hacking?
Growth hackers explore new growth opportunities systematically at any point of the customer journey, from awareness through the market to brand ambassadors by optimizing the product.
In terms of technology, it originated in 2010 when Sean Ellis coined it is mostly used by startups because of its limited budgets and limited resources.
Since then, it has shown an incredible increase in popularization among large-scale and traditional businesses.
Companies like Shopify like Uber has their own head of growth and dedicated growth team. The growth hacker is based on an experiment-based, data-driven.
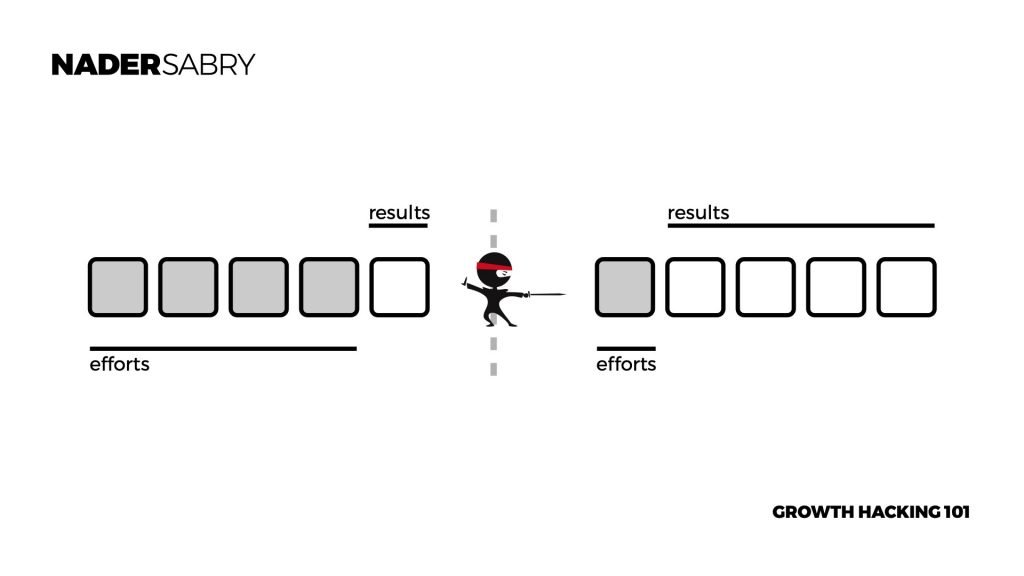
There is a wide range of definitions; in the Book Ready Set Growth, Hack growth hacking is defined at a strategic level as a process that achieved disproportional results.
This is best understood through an example of efforts v.s results. This is when less effort is exerted to get dispositional results.
How does growth hacking work?
As defined in the Ready Set Growth Hack, growth hacking is a systematic process governed by a concept called the growth cycle. the growth cycle is a three-phase process, where it starts with a growth problem, moves into experimentation then into scaling.
Based on this process, once a growth problem is well defined through a specific process it would then be up to the growth hacker to find solutions. Solutions are found vis structured and systematic experimentations.
Using growth analytics for data-driven growth decisions, growth hackers can quickly discover what works and doesn’t before investing a penny in more development. This is governed by a process called growth thinking which is a design methodology used for growth hacking.
Break the rules – growth hacking
The hidden weapons of growth hacking are simple and simple: Be a rule-breaker. The job requires you to think outside the box and unleash your creativity.
A growth hack involves having the right mindset on growth.
This job requires creativity and ad-hoc experiment with hypotheses and high potential. Be creative growth Hacks won’t come with any rules.
Rule-breaking is at the core of growth thinking and how the growth hacking process works.
- if a rule is working, find a better way to break I
- If a rule isn’t working, break it with a better one
- If a rule is about to fail, let it and then break it
- If a rule is about to have success, break that too
The growth hacking mindset or growth mindset is a very different way of working than that of other professions. Their goal is the north star metric which is basically a growth goal and only a growth goal.
Subscribe for updates
Four types of growth hacks
These four areas can be seen as a guide to answering the question “where to find a growth hack.” This guiding question sets the tone and process for finding, executing, and creating new growth hacks.
The optimization point is the target for deciding which of the four growth hacks best suits a situation. Through our research, we have found the optimization point is best measured by
- Speed of execution – how fast and effective you can action your growth hack.
- Level of flexibility to adjust – how fast and accurately you can change
- Cost of execution – how to keep execution cost-effective
- Return on investment – how to lower cost, efforts, and time against the results
In optimizing growth hacking, we look at the four types of growth hacks. There are four types of growth hacks they seek to exploit:
In optimizing growth hacking, we look at the four types of growth hacks. There are four types of growth hacks they seek to exploit:
- Find a limitation – an area not being solved well enough.
- Find a gap – an area not being solved at all.
- Find a hole – an area where its completely dysfunctional
- Find a combo – an area where a combination has not been exploited.
The most exploited type of growth hack is gaps, while combinations are the least executed. Although gaps might rise to the tide on this, that’s because they are the easiest to identify and execute. In complete contrast, the combinations are the least exploited due to complexity, lack of vision, and a willingness to try new things.
Business methodologies
Growth acceleration is one of the four types of methodologies used in the practice of management. The growth accelerator space is the most underdeveloped of the four types that being:
- Offering design models to design products and services
- Managing projects models design to manage development
- Building a company models design for building a company
- Accelerating Growth models designed to accelerate the growth process
To learn more about business methodologies and how they work, click here to learn more.
How does the growth hacking process work? – mastering the process for exponential growth.
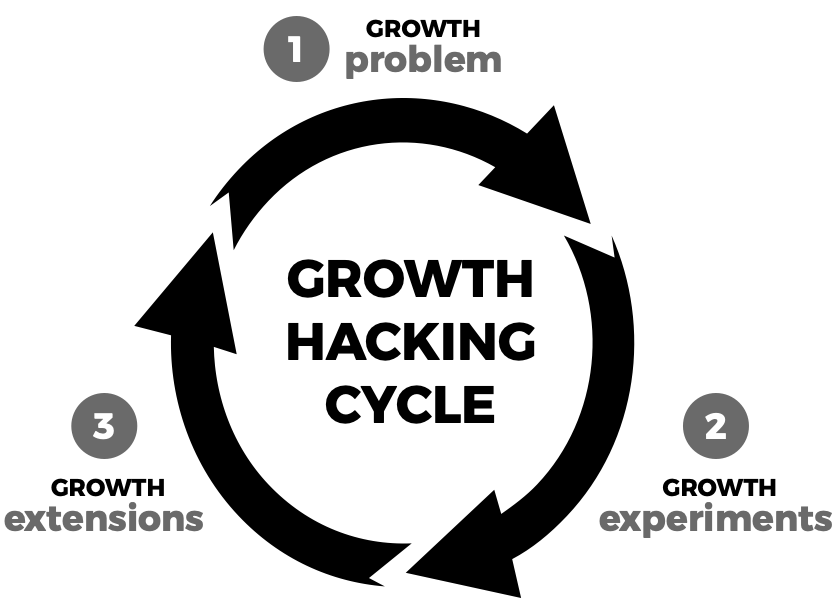
Growth hacking is a cyclical process. This process is divided into three phases the group problem growth experimentations ingrowth extensions. The company nation of these three phases is or how growth hacking actually works.
The final result of growth hacking which is always important to keep in mind, is exponential growth. The entire process of growth hacking is based on these three faces.
Exponential growth is about gaining non-incremental growth capabilities. The secret behind it the home is working incrementally to start with, and then building momentum through a compound in the process will master the growth hacking cycle.
This whole cycle needs to be undertaken from an ethical hacking perspective.
The growth problem – growth process
Before being able to hack growth, you must understand what your growth problem actually is. This is critical because it’s important to be specific and focused. Usually, there is a large growth problem at play.
However, without breaking the problem down and tackling smaller parts, you won’t solve the larger growth problem itself.
Consider this phase kind of like the concept of garbage in garbage out. If the guiding inputs are unclear or well defined or there is any distortion, then the remaining process will not work very well.
In fact, 85% of gross hacks fail because the growth problem at South has not been well defined enough.
Having clarity around your growth problem helps you solve over half of the growth hacking process. Knowing your growth problem in detail enables you to explore more growth hacking experiments better to take you to the next level.
14 growth problems areas to solve for
The following are 14 areas or areas that you would need to explore from a functional perspective to understand the depth of your growth problem.
Identifying where the actual growth problem starts as part of it and identifying the impact on other functions allows you to think and work from across functional perspectives.
- Financial
- Strategy
- Marketing
- Sales
- Management
- Competition
- Technology
- Recruitment
- Culture
- Structure
- Product/Service
- Team
- Operation
- R&D
Using these 14 areas as your guide will help your den if I were to start and go. The secret to it is identifying the cross-functional relationship that is affecting your growth. By doing that, you can understand all the components that relate to your growth problem in one shot.
Subscribe for updates
The growth experiment – growth process
Growth experimentation is at the corner of the growth hacking process. Ultimately growth hacker has no idea how the customer is going to respond.
The growth hacker may have some estimations or ideas on how to do that. But in reality, an experiment will not actually know if there is a possibility for growth.
One of the secrets behind this, as we experiment, is that we are looking for signals, not results. Seeking signals give a quick and low-cost indicator is there is a probability to find results.
This Ables is a growth hacker to makes quick, low-cost, and effective decisions within the experimentation process.
Maintaining access to good data throughout the process is vital. This process of maintaining access to all forms of data can be sued and reused in multiple ways without investing more money into collecting and using more data.
Gaining access to low-cost external data is vital to the process, but gaining external data should not be the only source.
Therefore maintaining access and gaining access to both internal and external data will be one of the most challenging balancing acts for a growth hacker.
Fail. pass learning system
The FPL system is designed to capture both pass and fail experiments’ learning and then transform them into new ideas that become growth hacks. This way, you have a sustainable system of capturing, designing, and testing new growth hacks throughout the exercise.
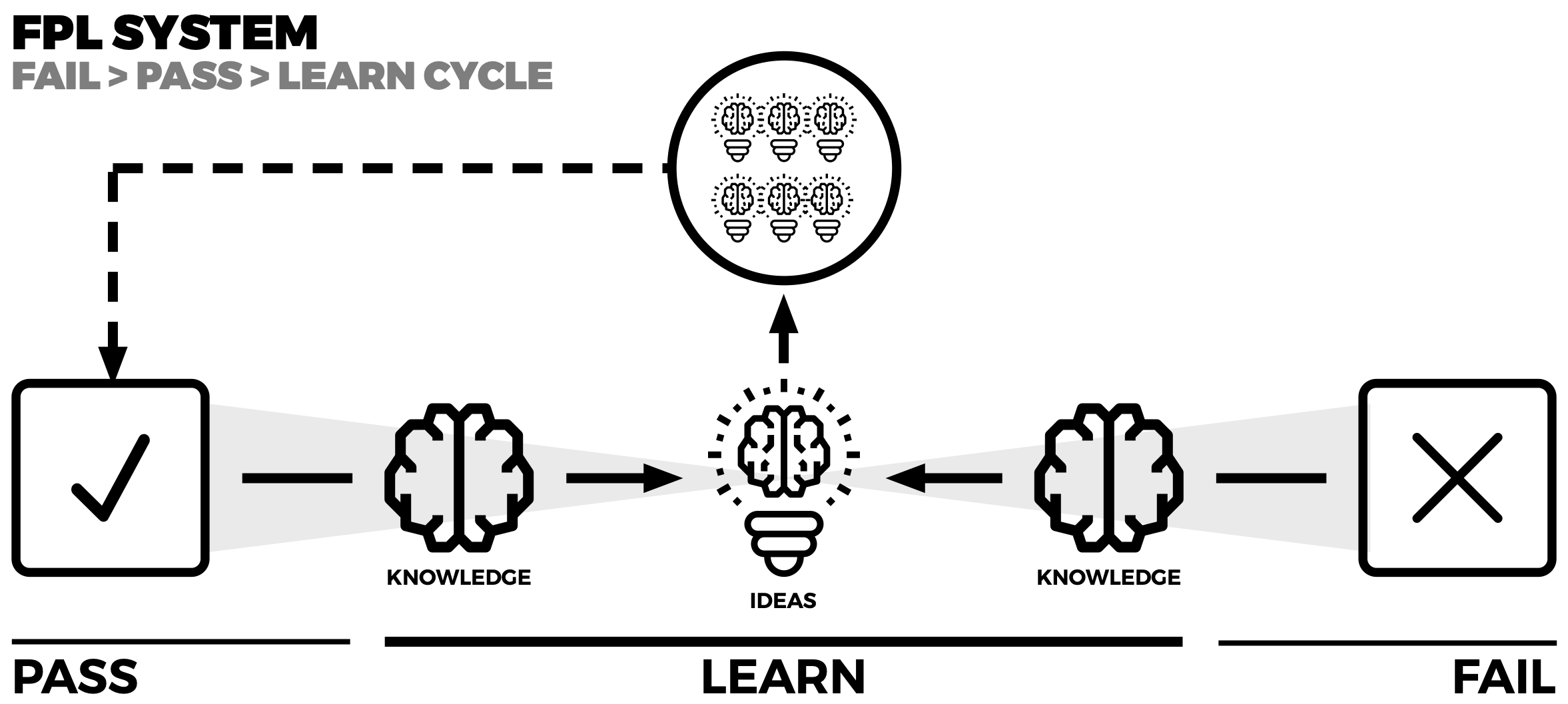
The essence behind the system is how to take a fail or pass and recycle it into something tangible. This enables a growth hacker to generate several different ideas. The flow of good-quality ideas is crucial for testing purposes.
If an experiment passes, then there are some structured perspectives on how to grow on the success. Equally so, with and failed experiment, the learning behind it drives many new ideas for growth tax.
The growth extension – growth process
Extended growth hacking is designed to extract more value from your existing experiments systematically. It is about generating new growth hacking ideas based on the current experiments, whether they have failed or passed, and their associated learning.
Based on the FPL system, we can look at six different elements when extending on growth hacks. These elements are all designed to create scale.
6 ways to expand your growth
Although scale can be misleading, the highest form of failure is at the end of the growth hacking process when someone is trying to scale. The following six elements are areas to look at when extending the gross hacks generated under the experiments.
1. Experiments
2. Wildcards
3. Adjustment
4. Pain Points
5. Combinations
6. New Growth Hacks
These six elements systematically provide a way to work with failures and passes in the learning system. As clearly demonstrated in the best-selling Ready Set Growth Hack, which gives deeper insight into using this system.
Some Dos and Don’ts for Growth Hacking Experiments
When setting out with your growth hacking experiments, it’s just as helpful to know what not to do as it is to know what will work. Here are some dos and don’ts to ensure you get the most out of your early experiments:
Do
1. Experiment with tactics.
2. Focus attention and resources on what’s working.
3. Invite feedback from users at all stages.
4. Look at analytics and data.
5. Be decisive.
Don’t
1. Don’t put too much money into one resource.
2. Don’t spend too long on one tactic or idea.
3. Don’t ignore data, especially churn rates.
4. Don’t hesitate on an idea.
5. Don’t worry about long-term strategies (yet).
In the beginning, growth hacking is about trying different tactics to see what works.
During this phase, the prospectors on your team will be the most valuable, as they will be experimenting and finding different ways to promote your product and brand.
Subscribe for updates
Understanding Scalability
There are three classifications of scalability: scalable, semi-scalable, and non-scalable.
1. Scalable refers to elements that can be scaled but have not been scaled yet.
2. Semi-scalable products and services have scalable parts and parts that are not; they need to be combined to become scalable.
3. Non-scalable refers to parts that need to be completely transformed into scalable elements in your organization.
There are three characteristics to e
ensure you are scalable.
1. Repeatability: Do you have a set of actions that can be duplicated?
2. No distortion: As you repeat, do quality and value stay consistent?
3. Longevity: The lifespan must be long-term, not short-term.
If your systems and process cannot be repeated without distortion in the context of a long-time span, you will not be able to scale.
At the core of scalability is automation, systems that allow automating the execution of repeated routines while supporting and driving non-routine processes.
Topline vs. Bottom line growth and growth hacking
Growth hacking techniques focus on increasing the top line rather than the bottom line by increasing sales, app downloads, and other cash-creating activities.
In short, growth hacking prioritizes revenue as the driver of growth (Figures 15).
Growth hackers focus on top-line efforts to drive the gross revenue of an organization. Although profitability is important, it will not be sustainable if a growth hack is too costly with time.
Gross revenue-driven activities are a priority, but ensuring they are profitable is important.
Now that we’ve learned some mechanics behind how growth hacking works and discovered some of the key components and values let’s look at how growth hacking actually happens.
To do this, we need to learn the tools of the trade.
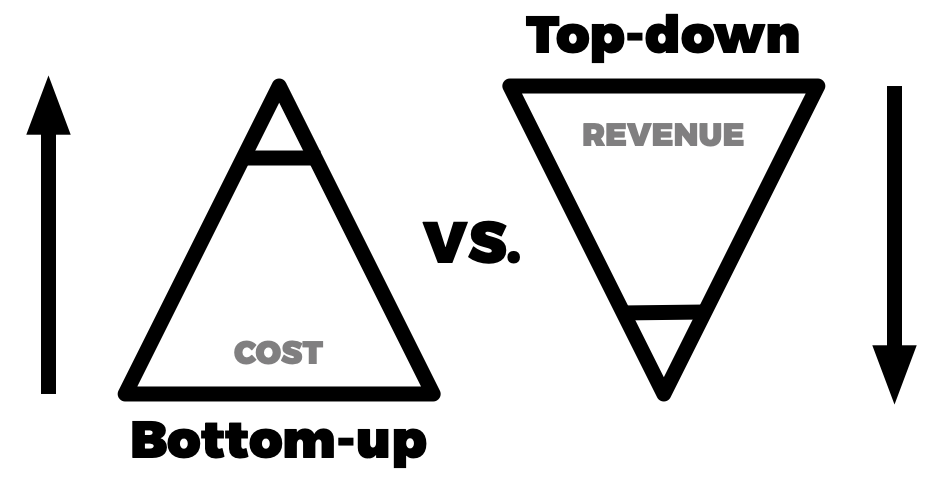
Top-line vs. bottom-line approaches
The following is a comparative perspective highlighting for you the difference between a topline growth approach versus a bottom-line growth approach.
Roughly 1 to 3% of organizations focus on topline growth, where the remaining focus is on traditional bottom-line activities.
Fundamentally the difference is that topline growth is based on increasing the boundaries of revenue. This is tales the development of new revenue streams models and even the acquisition of new resources and assets that enable top-line revenue growth.
Bottom line growth activities are usually cost-driven exercises. In essence, a bottom-line approach is re-organizing the resources and assets already in place to gain the best form of efficiency.
The ideal scenario is a good mix between the top and bottom-line activities. The issue is that most organizations go for the lowest hanging fruit, which happens to be bottom-line activities.
To gain a significant competitive advantage, it will be crucial for organizations to focus on the 1 to 3% of topline revenue development activities for growth.
Strategy
- Top-line: Focused on developing new sources of revenue
- Bottom-line: Over-dependent on existing revenue streams
Gross revenue
- Top-line: The primary driver is fresh and new sources of revenue
- Bottom-line: The primary driver is cost-cutting, then efficiency
Net revenue
- Top-line: Revenue is a priority; costs are secondary
- Bottom-line: Costs are primary; revenue is secondary
Cost structure
- Top-line: Improved and adjusted; with time, gain more profitability
- Bottom-line: Adjusted immediately, but less profitable with time
Growth hacking
- Top-line: Primary approach; this is the source of results with the most impact
- Bottom-line: Secondary approach; this supports primary growth activities and scaling
Summary of top vs. bottom-line growth
- Top-line: Top-line driven growth promotes innovation and disruption to build new revenue streams and even new business models
- Bottom-line: Bottom-line growth focus on costs and efficiency, which are important but are not enough to grow as they focus only on existing resources
Data to maintaining access and gaining access to growth opportunities.
Technologist Aaron Ginn describes a growth hacker as having “a mindset of data, creativity, and curiosity.” This curiosity is at the heart of growth hacking success.
Trying out new methods and testing them to see what works is the fundamental job of a growth hacker. By doing so, we can find methods that lead to rapid and cost-effective hyper-growth.
Growth hacking is the point at which the relationship between your efforts and your results is transformed.
It’s a shortcut to growth. It’s about taking an untried growth technique, testing it, learning from it, then scaling what works to maximize its utility.
Experimentation is at the core of this process so that more and more growth hacks can be discovered.
It’s important to note that growth hacking isn’t isolated to digital methods. Although digital means are vital to making a growth hack work, growth hacking is not digital per see.
Instead, I’d like you to think of any growth hack as having the following characteristics:
1. Fast — can be used to convert customers in a short amount of time
2. Cost-effective — experiments don’t require significant funding
3. Repeatable — can be repeated rapidly to deliver the same or better results
4. Flexible — can be adapted quickly and still maintain characteristics 1–3
5. Measurable — can be analyzed at a granular level to enable profound learning
Experimentation is key to find what growth hacks will work.
Subscribe for updates
What is ethical hacking?
Stephen King, president of the European Economic & Community Code, gave the webinar on five phases of moral hacking to the media.
He explains how malware hackers exploit the vulnerabilities of computers to hack into network storage if the computers were compromised.
According to King, when you want to beat a hacker, you must think like a hacker. As of December 2018, all hackers and hacked applications have a specific scope of an attack, and hackers have a unique capability to destroy data and cause billions of dollars.
Conversely, ethical hacking involves deploying a similar hacking approach with the same tools before being exploited.
The future of ethical hacking?
According to King, ethical hacking is still unknown to most audiences. King thinks that AI hack attacks are the next potential danger.
In other words, systems will need to defend themselves to AI hacks a bit in a different fashion.
AI hacks will next be potential threats to systems due to how they are designed to shield themselves from the threat posed by AI hacks, King said. Systems should be able to.
the ethical hacker
An ethical hacker is a growth hacker who engaged in white hat activities. This means they don’t engage in illegal activities or even grey areas.
Ethical hacking or an ethical hacker is essential to running a credible organization.
One of the main issues with unethical hacking is the price to be paid. With illegal activities, regulators clap down ard on those who violate.
Many police and law enforcement bodies do not have groups of hackers,s including ethical hackers who work with the police to identify, qualify, and prosecute those who break cyber security laws.
Cyber security is a quickly evolving area in law enforcement. As Hatters start using more sophisticated techniques tools, cyber security units need to be ahead of the crew.
Don’t target everyone with growth hacking.
Every new product, every innovative product, has a life cycle. To reach the majority of people, your product must then successfully pass through innovation and early adopters.
These are small groups that need to be specifically targeted.
If you’re targeting everybody, but they already want something you can barely sell it to because you’re not sure you are selling to.
How can I get it right? How do I do something? Tell me an e-nachbarb? Which is your connect the two with Airbnb?
Tell me the secret or shared value that the pair have between them and others? And if the market for your product is everybody, you can’t tell who is your target user.
Retention through growth hacking
Adobe says repeat customers are more likely to convert and spend more money. When using Facebook with Facebook, a 2016 study found the ROI was high. Facebook ads unveiled native integration with MailChimp.
In-App messages let us show you the fastest approach to sending messages immediately after clicking on your website.
You can also connect between platforms, so remarketing campaign messaging can coincide with marketing automation emails on platforms like Zapier. And you can manage them using Google Adwords, LinkedIn, and tweets. You can choreograph campaigns in advance according to user behavior.
Use customer feedback to create an excellent product.
Crazy Egg is a company that offers a wide range of marketing and site optimizing tools to increase customer satisfaction.
Neil Patel conducted customer interviews before launching an online product. By the time they introduced their services five months earlier, the firm had created a waiting list of 10,000 users ready to pay if they had paid.
They use their collection of feedback in the hope of improving their services. Each time they updated their services, the company publicly shared this news with their goal customers. By the end of the year, the company had a waitlist of 10 million customers eager to buy from The Crazy Egg Company.
Identify a North Star Metric
North Star Metric represents the average value delivered to customers. According to Airbnb, for example, the NSM represents the number of nights that were reserved.
Getting your team around an NSM can be beneficial. To refine your growth equation and narrow your focus, it’s best to select one critical metric of ultimate success all growth activity should be focused on,” advises Sean Ellis.
Once your team has formed a consensus on a metric that leads to long-term sustainable growth, it’s time to jump on to the process of accelerated growth.
The growth hacker and making the growth hacking process work.
The center of the universe in growth hacking is the growth hacker themself. The growth hacker is a different breed of talent emerging in today’s world. In fact, growth hacking is a super skill of the future.
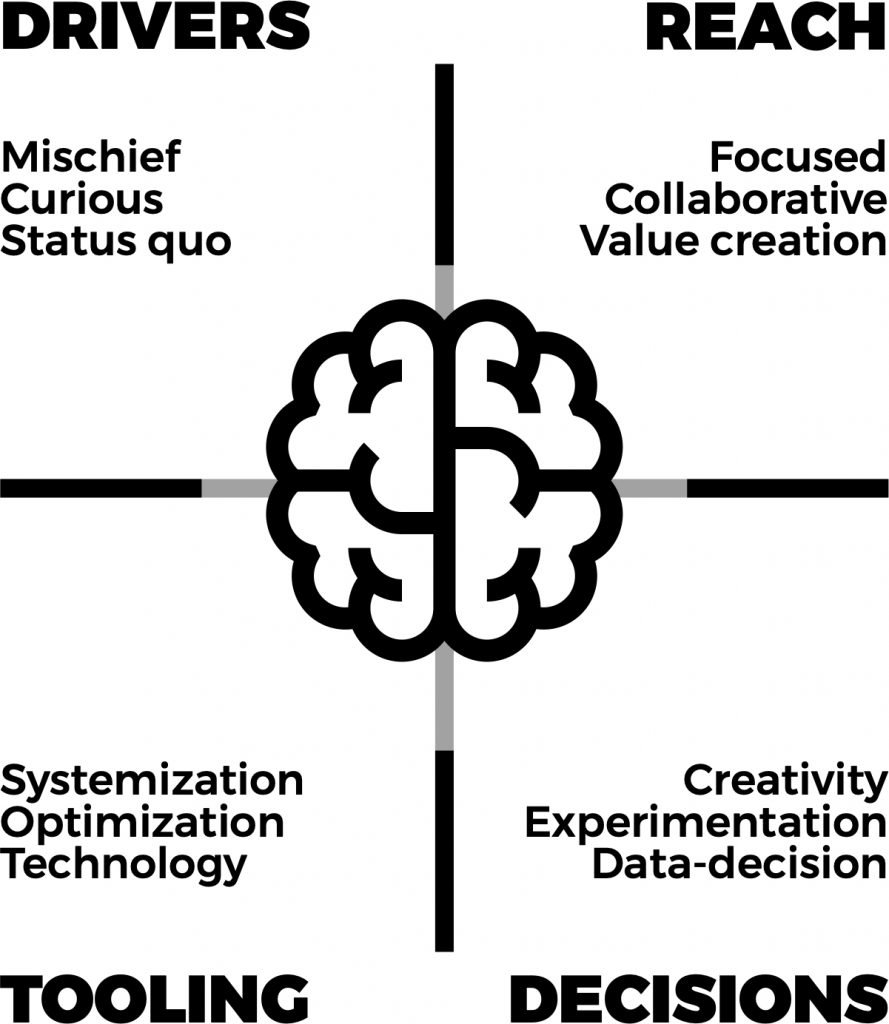
What is the Growth hacker mindset?
Four main taxonomies determine a growth hacker’s mind: driver’s reach, decisions, and tools. The combination of the four forms the underlying idea of aching disproportionate results.
Consider these habits to build a growth tribe, and a growth tribe is all about those who come together on common interests and traits.
The following will give you some insight into that. They align on the growth process, which is the glue that brings all this together.
You can safely say that experienced growth hackers 85% of the following are in place as well — let’s take a deep dive and an in-depth look into this.
1. Drivers
The drivers are the underlying motivations and stimuli that inspire how growth hackers think and take action.
Mischiefness
They deeply need to break the rules, as they do not believe in the rules they have not benefited from governing and limiting their way of life.
Therefore this underpins their thinking to find a way to break the rules to their benefit.
Curiosity
They are fascinated by digging deeper into how things work by asking the big why questions.
This allows them to understand theories and phenomena better to map out their mechanics to manipulate them toward their benefit.
Status quo
The general rules over institutionalization drive their need to challenge the establishments surrounding them.
This allows them to break the rules and change the norms of how society around them works.
2. Reach
Growth hackers have a goal to reach as many people as possible without the general population knowing how they did it.
Focused
They have a too-focused approach by pinning done abstract problems and creating unique structures to solve them.
Collaborative
They have a resourceful approach where they work with like-minded people and find other cross-functional people to reach their goals effectively.
Value-creation
They focus on creating value with monetization, often trying to reach the masses to make a change.
3. Decisions
When hacking growth optimization is the goal to solve at a high level, there is no one solution to a single problem but finding the fastest, easiest, and cheapest way.
Creativity
Growth hackers are resourceful; they find simple, fast, and digestible ways to solve problems. One of the challenges for growth hackers is thinking too technically.
Experimentation
They run tests and lots of them to determine the most optimal approach to getting results using all possible avenues.
Data-driven
They make decisions based on data, even if the data might potentially be blinding. Data helps determine the most optimal options.
4. Tools
Growth hackers are always seeking new tools, optimizing existing ones, and finding optimal ways to connect them to solutions.
Systemization
For a solution to work, it needs to be automated, and when automated, the probability of scalability is a lot higher when seeking exponential GrowthGrowth.
Optimization
When finding the right tools and connecting them, the goals are optimizing the way they work together. This holistic approach helps maximize optimization.
Technology
Technology enables automation, scalability, and integration, which underpins GrowthGrowth even if you’re a non-tech company.
The mindset of a growth hacker is defined by how they solve problems. The elements described above are the most common thinking patterns of growth hackers.
14-Growth hacker habits
Growth hackers have 14 critical habits they work with. They do not work with all of them as a strength at once.
You will find a single strength supported by three other habits and the rest for development over time. The 14 habits are:
- Openness
- Flexibility
- No ego
- Risk-taking
- Fresh perspective
- Generosity
- Curiosity
- Team focused
- Listen before action
- Cohesive approach
- Consensus
- Diplomatic
- Action driven
- Collective win
Remember that these habits help support the T-shaped skills.
Openness
They use an open approach to gain resources, using them, and find solutions to growth problems. This often is the underpinning factor behind their creativity.
Flexibility
When using an open approach, they work flexibly to solve growth problems knowing they don’t have the exact solution but need to be flexible in finding it.
No ego
They focus on removing their ego from the equation; this is often challenged by technical thinking – blinding them to find creative solutions.
Risk-taking
They take bold yet calculated risks, often progressive, to manage unknown facts that are not seen early on.
Fresh perspective
They focus on finding new ways to solve existing problems by finding new solutions not yet attempted or poorly executed.
Generosity
They are open-handed to negotiate and broker the acquisition of new resources by being generous to open new doors.
Curiosity
They look deep into the whys. This helps them find unseen possibilities not seen by asking excellent questions and often challenging the status quo.
Team focused
They often are challenged with trust, but they thrive by forming collective learning and efforts when they develop their small groups of trusted people.
Listen before action
They focus on getting useful quality information before managing their risks and coming up with better growth hacks quicker and easier.
Cohesive approach
They focus on developing networks beyond their teams for the exchange of know-how and cross-development opportunities.
Consensus
They focus on developing a common approach to ensure buy-in and momentum to generate the energy needed to undertake large initiatives.
Diplomatic
They are often challenged with being diplomatic, which is key to ensuring relationships supersede technical barriers to solutions.
Action driven
All their know-how and tools are geared towards taking action, leaving little space for theories that waste time and do not get results.
Collective wins
Finding ways that everyone wins in the process, including those directly involved, even if their role is minor in the overall outcome.
These 14 habits are specific to growth hackers; they often draw on these habits as their core capability. With the focus on a single superpower among these habits, growth hackers must develop their habits.
Subscribe for updates
Growth hackers think outside the box.
PayPal decided the payment would be to people who signed up and referred friends. The hacking boosted PayPal’s Customer base from 7% to 10% daily.
In other words, PayPal jumped. Within weeks, PayPal has surpassed 5 million users.
Other startup founders may have thought of it as suicide, especially when you consider that most startups are strapped for cash, but PayPal’s founders went with it.
The growth hacker is comfortable with trying an idea no matter how ridiculous or absurd.
Growth hackers are resilient.
A growth hacker knows that experimentation does not turn out to be perfect. Some of these are going to be absolute failures. But those problems won’t end them.
Instead, they have to experiment with different strategies to find the one they think will bring exponential growth to the startup.
Growth hackers are focused on growth.
Sean Ellis referred to growth-hackers as people whose north is growth.
Only identifying and analyzing your potential growth is what is required to scale your company.
Why do organizations recruit ethical hackers?
Organizations have hired hackers so that they can prevent hacking. Organizations need at least one month to discover that hackers are ravaging their systems.
Ethical hackers have to detect weaknesses in the systems that could affect their work and review security practices with industry standards.
Afterward, a firm will be responsible for analyzing and strengthening security policies, network infrastructure, and end-user practices to guard the company against cyber threats. King. King said ethical hacking was legal in the United States and helped defend and not attack the systems.
the growth team
a good growth team masters the idea to maintain access and gain access to top-quality data. With the cental skill around growth experiments. growth experiments essential to the development of a good growth team.
Good growth experiments practices enable a growth team to filter through data and find what works and doesn’t. Other data-gathering equipment and tools have always to be used to use the best possible channels to gain access and maintain access to data.
Multiple email accounts enable growth hackers to gain access and maintain access to several data sources like scrapping websites and other data platforms and maintain a distance between them and the acquisition source of data.
Some of the challenges are good growth team needs to focus on are:
- the onboarding process
- os details and other tech information for hacking purposes
- ensure all team members are trained up and up to date on all practices being used
- have a good list of future exploitation always ready to go
- have good tools for traces leading to ensure cyber security
- ensure the growth process works in a sequential manner
- have a good set of multiple e mail accounts and user accounts
- gained access to all major tools to be sued at all times
- always give paying customers priority and new users
- understand potential customers very well and find more customers like them
- have a well-defined customer acquisition process
- conduct regular vulnerability scanners for cyber security purposes and port scanners
- hacker finds valuable information constantly
- always be ready to challenge your existing business model
- experiment fails are your best source of the next big ideas and rank ideas
- good sales team integration
- lost revenue is the best place to start find growth hacks and exploitations
- get big on referral traffic
- well defined acquisition channels
- keep focused on vulnerability scanning all the time
- always be active in information gathered
- use the search engine wisely to get as much organic traffic as possible
- always have the entire team involved
- optimize your entire website don’t leave anything unoptimized
- Use many IP addresses, especially IPV6 protocols
- scan data and modify data at all times
- instant messages and chatbots are big; don’t overlook them
———–
Introduction to growth thinking growth by design, how to thinking design, and growth hack.
GROWTH BY DESIGN – Most Growth Hackers struggle to get traction for new ideas. A lack of guidance and exact next steps are to blame.
Imagine if you could grow a new idea from beginning to end, with a framework to move from idea and action in a fast, simple, and low-cost approach.
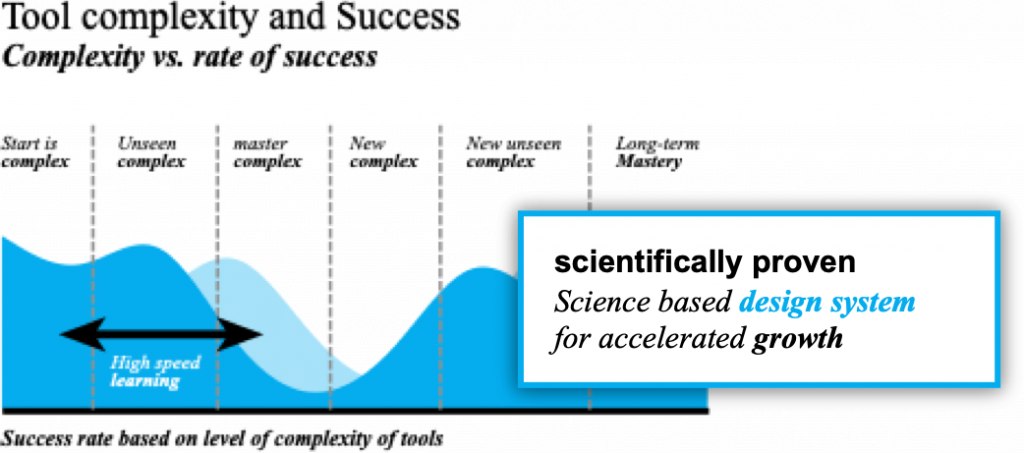
Actioning ideas with precision isn’t easy; with the growth thinking, science-backed design system built by the top minds in growth hacking, it’s a simple, well-structured yet creative system that allows you to find growth.
Growth thinking is a fast, easy, and simple way to prototype growth hacks. This enables growth by visualizing a growth hack in abstract and then detailing them into a systematic approach.
This makes it easy to develop and improve growth hacks and generate new, better growth hacks.
Benefits of the growth thinking design methodology —
1. From idea to action – accurately and rapidly turn growth hacking ideas into execution quickly and cost-effectively,
2. Think at scale – quickly and effortlessly find methods to take an abstract growth hack, structure it, scale it, and
3. Save time and money – rapidly prototype your growth hacking ideas saving time and money.
This methodology uses a design system that Visualization, Systemize, Optimization, helps Rapid development, and instills Collaboration.
How to get started with growth thinking
The methodology and system are based on the book itself. Your starting point is to buy the book, but here is the best part if you buy the book, you’re supported with over $300 in free training support from the quick start to basic skill-building, and the top 10 secrets advance your growth thinking skills.
Buy the book click here.
See the training click here.
Let’s get started!





